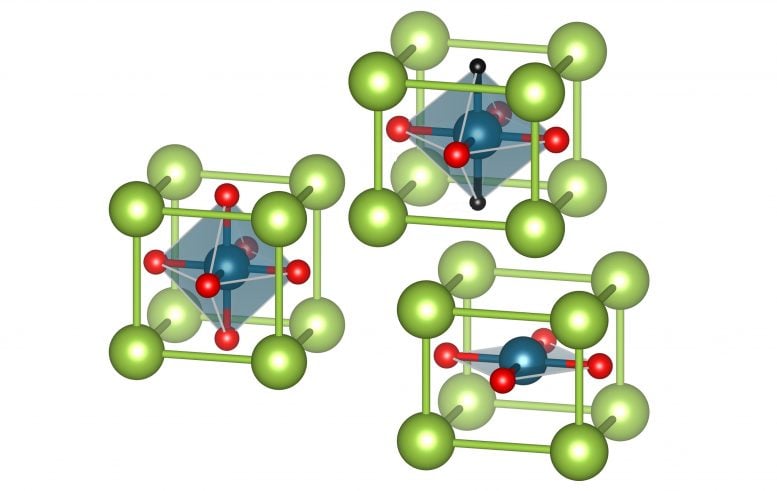
When hydrogen is incorporated into the nickelate structure, it is not a superconductor. Credit: TU Wien
Nickel is supposed to herald a new age of superconductivity – but this is proving more difficult than expected. Scientists at TU Wien (Vienna) can now explain why.
Last summer, a new age for high-temperature superconductivity was proclaimed — the nickel age. It was discovered that there are promising superconductors in a special class of materials, the so-called nickelates, which can conduct electric current without any resistance even at high temperatures.
However, it soon became apparent that these initially spectacular results from Stanford could not be reproduced by other research groups. TU Wien (Vienna) has now found the reason for this: In some nickelates additional hydrogen atoms are incorporated into the material structure. This completely changes the electrical behavior of the material. In the production of the new superconductors, this effect must now be taken into account.
The search for High-Temperature Superconductors
Some materials are only superconducting near absolute temperature zero — such superconductors are not suitable for technical applications. Therefore, for decades, people have been looking for materials that remain superconducting even at higher temperatures. In the 1980s, “high-temperature superconductors” were discovered. What is referred to as “high temperatures” in this context, however, is still very cold: even high-temperature superconductors must be cooled strongly in order to obtain their superconducting properties. Therefore, the search for new superconductors at even higher temperatures continues.
“For a long time, special attention was paid to so-called cuprates, i.e. compounds containing copper. This is why we also speak of the copper age,” explains Prof. Karsten Held from the Institute of Solid State Physics at TU Wien. “With these cuprates, some important progress was made, even though there are still many open questions in the theory of high-temperature superconductivity today.”
But for some time now, other possibilities have also been under consideration. There was already a so-called “iron age” based on iron-containing superconductors. In summer 2019, the research group of Harold Y. Hwang’s research group from Stanford then succeeded in demonstrating high-temperature superconductivity in nickelates. “Based on our calculations, we already proposed nickelates as superconductors 10 years ago, but they were somewhat different from the ones that have now been discovered. They are related to cuprates, but contain nickel instead of copper atoms,” says Karsten Held.
The Trouble with Hydrogen
After some initial enthusiasm, however, it has become apparent in recent months that nickelate superconductors are more difficult to produce than initially thought. Other research groups reported that their nickelates do not have superconducting properties. This apparent contradiction has now been clarified at TU Wien.
“We analyzed the nickelates with the help of supercomputers and found that they are extremely receptive to hydrogen into the material,” reports Liang Si (TU Vienna). In the synthesis of certain nickelates, hydrogen atoms can be incorporated, which completely changes the electronic properties of the material. “However, this does not happen with all nickelates,” says Liang Si, “Our calculations show that for most of them, it is energetically more favorable to incorporate hydrogen, but not for the nickelates from Stanford. Even small changes in the synthesis conditions can make a difference.” Last Friday (on 24.04.2020) the group around Ariando Ariando from the NUS Singapore could report that they also succeeded in producing superconducting nickelates. They let the hydrogen that is released in the production process escape immediately.
Calculating the Critical Temperature with Supercomputers
At TU Wien new computer calculation methods are being developed and used to understand and predict the properties of nickelates. “Since a large number of quantum-physical particles always play a role here at the same time, the calculations are extremely complex,” says Liang Si, “But by combining different methods, we are now even able to estimate the critical temperature up to which the various materials are superconducting. Such reliable calculations have not been possible before.”
In particular, the team at TU Wien was able to calculate the allowed range of strontium concentration for which the nickelates are superconducting — and this prediction has now been confirmed in experiment.
“High-temperature superconductivity is an extremely complex and difficult field of research,” says Karsten Held. “The new nickelate superconductors, together with our theoretical understanding and the predictive power of computer calculations, open up a whole new perspective on the great dream of solid state physics: a superconductor at ambient temperature that hence works without any cooling.”
Reference: “Topotactic Hydrogen in Nickelate Superconductors and Akin Infinite-Layer Oxides ABO2” by Liang Si, Wen Xiao, Josef Kaufmann, Jan M. Tomczak, Yi Lu, Zhicheng Zhong and Karsten Held, 22 April 2020, Physical Review Letters.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.166402