HPQ Silicon Inc., a technology company based in Montreal, is making waves with a groundbreaking advancement in fumed silica production that promises to disrupt the industry. Fumed silica, a versatile material used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and construction, traditionally involves energy-intensive and environmentally taxing processes. However, HPQ’s innovative technology is not only reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions dramatically but also setting a new standard for sustainability in manufacturing.
Background and Context
Founded with a mission to revolutionize the production of silicon and silica-based materials, HPQ Silicon has been steadily gaining traction in the green technology space. The company’s latest announcement comes after years of development in collaboration with PyroGenesis Canada Inc., a leader in plasma-based technology. This partnership has led to the creation of HPQ’s Fumed Silica Reactor (FSR), which promises to reshape the fumed silica market by introducing a more efficient and environmentally friendly production method.
Key Highlights and Advantages
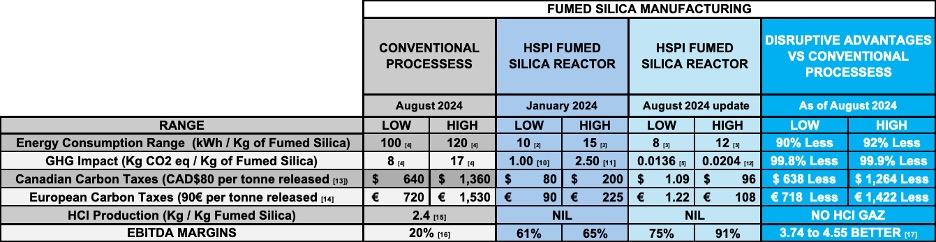
HPQ’s Fumed Silica Reactor stands out due to its significant reductions in energy use and carbon emissions. According to newly released data, the FSR requires up to 92% less energy than conventional methods, which typically consume between 100 and 120 kWh per kilogram of fumed silica produced. Furthermore, the carbon footprint of the process has been slashed by up to 99.9%, representing a near-total elimination of CO2 emissions compared to traditional production methods. These advancements not only make HPQ’s fumed silica production more sustainable but also position the company as a leader in green manufacturing.
Updated Table Highlighting HSPI Disruptive Advantages
Potential Impact and Significance
The implications of HPQ’s technological breakthrough are vast. With global demand for fumed silica on the rise, particularly in industries committed to reducing their environmental impact, HPQ’s innovative process is likely to attract significant attention from investors and industry players alike. The ability to produce fumed silica more efficiently and with a drastically reduced environmental footprint opens new market opportunities and strengthens HPQ’s competitive edge. As the company transitions from pilot to commercial production, it is well-positioned to capture a significant share of the market.
Expert Opinions and Analysis
Industry experts are already taking note of HPQ’s potential to revolutionize fumed silica production. Bernard Tourillon, CEO of HPQ Silicon, emphasized the transformative nature of the FSR technology, stating, “In mature industries like fumed silica production, improvements are typically incremental. However, with our FSR technology, we are poised to disrupt the market by enhancing efficiency and reducing costs, potentially altering the competitive landscape.”
Challenges and Considerations
While the technological advancements are impressive, HPQ faces the challenge of scaling production to meet market demands. The transition from pilot plant to full-scale commercial operation will require careful management and further investment. Additionally, market acceptance of the new technology will be crucial. However, HPQ’s strong environmental credentials and potential cost savings offer compelling reasons for adoption.
Conclusion
HPQ Silicon’s advancements in fumed silica production represent a significant leap forward in sustainable manufacturing. By drastically reducing energy consumption and emissions, the company is not only setting a new industry standard but also positioning itself as a key player in the global push towards greener industrial processes. For investors and the broader business community, HPQ Silicon presents a compelling opportunity to be part of a transformative shift in the silicon and silica-based materials industry. As the company moves closer to full-scale commercialization, its impact on both the market and the environment is expected to be profound.
View original release:
https://hpqsilicon.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/HSPI_FSR_ENE_CO2_UPDATE_V_CL14.pdf