Anaconda Mining Reports Metallurgical Testing Results for the Goldboro Gold Project, Demonstrating Excellent Gold Recoveries
"We are extremely pleased with the results of the recently completed metallurgical testing program which reinforce the excellent recoveries achievable at Goldboro, and further support the potential for an expanded surface mining scenario for the Project. The metallurgical characteristics of the lower-grade mineralization adjacent to the higher-grade zones has demonstrated excellent recoveries which, combined with the previous metallurgical testing results, demonstrate a strong recovery curve for the Project. These positive results will be incorporated into the upcoming updated Mineral Resource Estimate anticipated in Q1 and will support the advancement of the feasibility study for the Goldboro Gold Project, where the impact of the strong recovery results and presence of significant background mineralization will be considered with respect to the mining rate, strip ratio, mill throughput, annual gold production and other key economic parameters."
~Kevin Bullock, President and CEO, Anaconda Mining Inc.
The results were produced from the recent metallurgical optimization and variability testing program completed by Base Metallurgical Laboratories in Kamloops, British Columbia under the overall supervision of Ausenco Engineering Canada Inc. Testing occurred in late 2020 on composite samples from near surface mineralization and included comminution testing, grind optimization, gravity concentration, leach testing, cyanide destruction and arsenic precipitation. Cyanide destruction and arsenic precipitation development were also completed to generate samples for environmental and geotechnical characterization studies supporting continued environmental permitting.
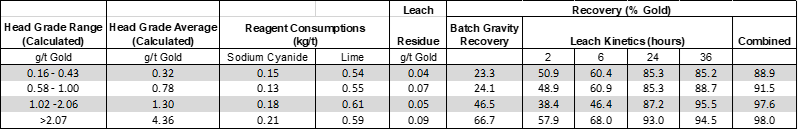
The Met Program evaluated 33 discrete composite samples ("composite" or "composites") representing 300 kilograms of material from across the deposit. Each composite consisted of multiple samples collected from diamond drill core, from within a specific grade range and from the three different gold systems within the deposit (West Goldbrook, Boston Richardson, and East Goldbrook). In total, the metallurgical program tested distinct grade bins, ranging from 0.16 g/t to 4.46 g/t gold (see Table 1 below) with an average grade of all composites at 1.04 g/t gold. Samples within each grade bin included material from across the deposit and from various portions of the deposit including modelled geological solids which include some high grade samples as well as lower grade material adjacent to modelled geological solids, representing all rock types observed in the deposit. The lower grade material represents a significant amount of mineralized material that was never previously tested, within or outside of the belts, particularly at or below 1.0 g/t, and the results of the Met Program on this material demonstrate excellent recoveries within these grade ranges.
Table 1. Results of the Met Program showing average grade, leach characteristics, gravity recovery, leach recovery and overall recovery of composites.
The results from this program (Exhibit A), combined with previous results announced in July 2019 (Exhibit A), demonstrate the exceptional linear recovery curves to be used for the upcoming Mineral Resource Estimate and ongoing Feasibility Study planned for Q4, 2021.
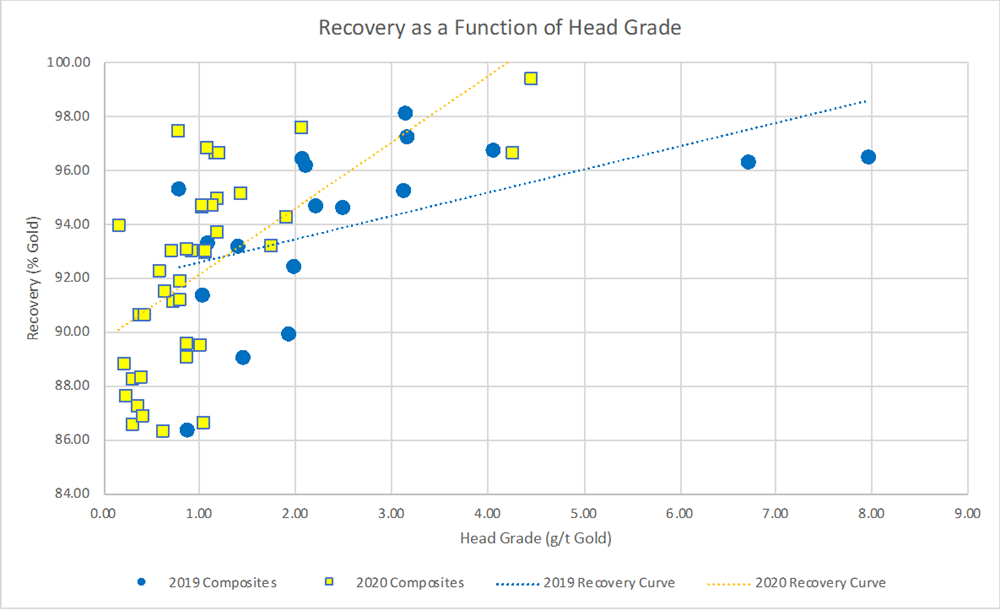
Exhibit A. A graph showing the recovery curves as a function of head grade from both the recent Met Program using background material (2020 Composites: Yellow Squares and Red line) as well as the 2019 metallurgical program which used only high-grade material (2019 Composites: Blue circles and line). Both higher grade mineralized material and lower grade background material show strong metallurgical recoveries.
Crushing and Grinding Testing
Detailed comminution testing characterized ore hardness by SMC (SAG Mill Comminution) Test, and Bond Rod Mill Work Index ("RWI"), Bond Ball Mill Work Index ("BWI") and Bond Abrasion Index ("AI"). The Composites fell in the range of 28.1 to 32.9 A x b values from the SMC tests, considered to be hard to very hard (resistance to impact breakage), and with a Bond Ball Mill Work Index median of 15.1 kilowatt hours per tonne ("kWh/t") which spanned the medium to medium-hard range of hardness. The average AI value was 0.228 g, which is low to medium abrasion.
Gravity Testing
An overall composite sample was tested with the Extended Gravity Recoverable Gold ("E-GRG") protocol to determine their amenability to gravity concentration. The results showed very high Gravity Recoverable Gold ("GRG") of 76% gold on a single overall composite. The GRG value is indicative of gravity gold amenability and indicates that all three Composite Ranges are amenable to recovery within a gravity circuit.
The GRG value does not directly predict or correlate gold recovery results from a closed-circuit milling operation.
Leach Testing
The flowsheet utilized in the Met Program consisted of grinding to a target of 80% passing 110 micron followed by combined gravity and leach for combined gold recovery as shown in the table above. Leach retention time of 36 hours was selected in optimization testing along with a slurry density of 45% solids and a sodium cyanide concentration of 0.5 grams per Litre ("g/L").
A total of 40 leach tests were conducted including initial screening tests and a bulk leach test. The results showed:
- Batch gravity recovery of gold ranging from 3% to 84%, averaging 26%;
- Gold leach extractions ranging from 80% to 96%, averaging 89%, with a final residue values of 0.01 g/t to 0.45 g/t gold, averaging 0.06 g/t gold;
- Combined overall gold extraction ranging from 86% to 99%, averaging 92%;
- Calculated gold head grades ranging from 0.16 g/t to 4.46 g/t gold, averaging 1.04 g/t gold; and
- Gold recovery was predictable over the entire range of composites including head grades and spatial distribution and by lithology.
Plant recoveries do not include typical plant losses.
Cyanide Destruction and Arsenic Precipitation
Cyanide destruction using the SO2/air method testing with batch and continuous testing demonstrated that a weak acid dissociable cyanide ("CNWAD") concentration below 3 milligrams per Litre ("mg/L") could be achieved with 45 minutes of retention time using a conventional addition ratio of 5.0g SO2/g CNWAD.
Arsenic precipitation of the Cyanide Destruction product with ferric sulphate reduced arsenic in solution to below 0.5 mg/L. Addition rates of ferric sulphate were in line with industrial practice at 8:1 iron to arsenic. This testing confirms that cyanide destruction and arsenic removal systems achieve water quality that meets the Federal Environmental Code of Practice for Metal Mines and the Metal Mining Effluent Regulations (MMER) discharge criteria.
Qualified Person
This news release has been reviewed and approved by Robert Raponi, P. Eng. of Ausenco Engineering Canada Inc.., a "Qualified Person", under National Instrument 43-101 Standard for Disclosure for Mineral Projects
ABOUT ANACONDA
Anaconda is a TSX and OTCQX-listed gold mining, development, and exploration company, focused in Atlantic Canada. The company operates mining and milling operations in the prolific Baie Verte Mining District of Newfoundland which includes the fully-permitted Pine Cove Mill, tailings facility and deep-water port, as well as ~15,000 hectares of highly prospective mineral lands including those adjacent to the past producing, high-grade Nugget Pond Mine at its Tilt Cove Gold Project. Anaconda is also developing the Goldboro Gold Project in Nova Scotia, a high-grade resource and the subject of an on-going feasibility study.