2024-06-10 07:01 ET - News Release
TORONTO, ON / ACCESSWIRE / June 10, 2024 / Theralase® Technologies Inc. ("Theralase®" or the "Company") (TSXV:TLT)(OTCQB:TLTFF), a clinical stage pharmaceutical company dedicated to the research and development of light and/or radiation activated small molecules for the safe and effective destruction of various cancers, bacteria and viruses, is pleased to announce that in preclinical research, it's lead compound, RuvidarTM, when combined with Bacillus Calmette-Gurin ("BCG"), was able to create a new compound with new synergistic characteristics.
In cell-based experiments, the new compound, nicknamed RuBCG, was able to significantly increase the efficacy of BCG in cancer cell kill versus BCG or RuvidarTM alone, when non-light activated.
The mechanism of action is believed to be through a reversal of the cell wall charge of the BCG bacteria and in return a significant enhancement of bladder cancer cell kill by RuBCG.
BCG is an attenuated form of Mycobacterium bovis, a bacterium with established efficacy in the treatment of urinary bladder cancer. It has been used clinically for decades, as the standard of care in the treatment of Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer ("NMIBC").
BCG is believed to work by invading bladder cancer cells and triggering an immune response, allowing the body's own immune system to attack and destroy the bladder cancer cells.
Unfortunately, BCG is effective in only 75% of patients treated and lacks a duration of response as 50% of these patients recur within 1 year of treatment.
A possible explanation for why BCG works for certain patients, fails in others and lacks a durable response may lie in the fact that BCG possesses a strong negative electrical charge. Cancer cells also possess a strong negative electrical charge. This results in the formation of a repulsion between the BCG bacterium and bladder cancer cells, which would thus make it difficult for BCG to adhere to and be absorbed by bladder cancer cells to affect a response. As a result, BCG remains unable to securely bind to the target bladder cancer cells and thus is ineffective in their destruction. This charge repulsion between BCG and bladder cancer cells is demonstrated clinically, by patients being required to undergo multiple BCG induction treatments, with high doses of BCG, in the hopes of achieving a meaningful anti-cancer effect.
A novel way to increase BCG effectiveness would be to "switch" the charge of negatively charged BCG to positively charged BCG, thus enabling bladder cancer cell adhesion and penetration of the negatively charged cancer cells.
As shown in Figure 1, when RuvidarTM was combined with BCG, it was able to reverse the negative charge of BCG to a positive charge, thus allowing potentially greater BCG uptake by NMIBC cells and a corresponding higher kill rate.
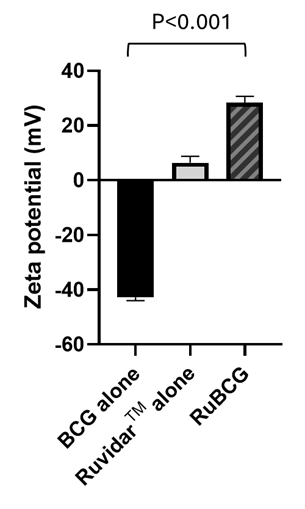
Figure 1: Inversion of BCG surface charge by RuvidarTM in RuBCG formulation (at 20 uM RuvidarTM and 0.04 mg/mL BCG).
Therefore, Theralase® has been able to demonstrate preclinically that RuvidarTM was able to override the negative surface charge of BCG making their attachment and uptake in NMIBC more efficient.
As shown in Figure 2, RuBCG was able to increase the immunogenicity (ability to produce an immune response) in bladder cancer cells, by significantly decreasing immune checkpoint inhibitor Programmed Death Ligand-1 ("PD-L1").

Figure 2: Increase in immunogenicity of T24 cells (human bladder cancer) upon incubation with RuBCG (at 30:1 BCG:T24 ratio and 20 uM RuvidarTM).
As shown in Figure 3, RuBCG increased cell kill of T24 (human bladder cancer cells) versus the individual toxicities of RuvidarTM or BCG alone, when non-light activated.

Figure 3: Increase in cytotoxicity of T24 (human bladder cancer cells) upon incubation with RuBCG (at 30:1 BCG:T24 ratio and 20 uM RuvidarTM).
Dr. Arkady Mandel, M.D., Ph.D., D.Sc., Chief Scientific Officer of Theralase® stated, "Treatment of NMIBC with BCG vaccine presents challenges, as proper uptake of the vaccine in bladder cancer cells requires the administration of high and multiple doses. The results presented today represent Theralase®'s commitment to unlocking the inherent value of the patented RuvidarTM compound for the benefit of the hundreds of thousands of patients, who are diagnosed with NMIBC, every year. Patients diagnosed with NMIBC face challenges in the treatment of their disease that this new research hopes to solve. In a human bladder cancer in-vitro model, Theralase® has been able to demonstrate a significant improvement in the efficacy of BCG, through the addition of RuvidarTM to form RuBCG. This new formulation eliminates the surface repelling charge of BCG cells and increases the immunogenic and cytotoxic effect on cancer cells (P=0.02 and <0.001, respectfully).The overall data indicates that RuBCG is capable of inducing both an immunogenic and synergistic destruction of bladder cancer cells, which is not attainable using BCG alone."
Dr. Mandel continued, "Peer-reviewed research has demonstrated that bacteria-based immunotherapy; including, naive bacteria, bacterial components and bacterial derivatives, are able to modulate immune responses via various cellular and molecular pathways; however, these promising methods of anticancer therapy are far from being optimized. The anti-cancer use of BCG can be compared to an uncut and unpolished gem, a "rough diamond" so to speak; however, in RuBCG, this "rough diamond" is finished displaying brilliant sparkle and fire resulting in targeted, synergistic killing of cancer cells and providing an opportunity to reverse the limitations of BCG alone. We expect that the new Theralase® proprietary formulations will enable the optimization of various bacterial-mediated tumor immunotherapies to enhance their value in numerous clinical applications".
Roger DuMoulin-White, B.Sc., P.Eng., Pro.Dir., President and Chief Executive Officer of Theralase® stated, "In this latest research, we have focused on the creation of a new compound that uses the unique characteristics of RuvidarTM to make an existing cancer therapy, such as BCG, much more effective. Based on the latest Theralase® research, RuBCG appears to have a very strong efficacy in the destruction of NMIBC."