A fiery debate rages among investors over the question of central bank stimulus. The question is whether the stock market needs stimulus in order to advance, and is stimulus only creating a bubble which will burst at some point and lead to depression?
Regardless of the philosophical rectitude of central bank intervention, there can be no denying its efficacy. The most fundamental truth of the financial market is that “liquidity, liquidity, liquidity” is the market’s lifeblood. Financial stimulus contains the seeds of recovery and will cure any bear market in equities, as I’ll attempt to prove in this commentary. The truth of this assertion can be found in the very wisdom of King Solomon, who in the book of Ecclesiastes wrote that “money answers all things.” Stocks will always, without exception, respond positively to stimulus – provide there are no countervailing obstacles in the way [e.g. tax increases, margin requirements].
Critics of stimulus often point to Japan as an example of how quantitative easing (QE) supposedly failed. Seventeen years ago the Bank of Japan (BOJ) led all other central banks by more than a decade with its zero-interest-rate policy, when its benchmark rate was lowered to zero for the first time during March 1999. As Dr. Ed Yardeni recently observed:
“The BOJ lagged behind the ECB by nearly 20 months, introducing its negative-interest-rate policy (NIRP) on January 29 of this year. The central bank was early with QE when it expanded its reserves balance starting during November 2001 through January 2006. That was just a warm-up act for the dramatic expansion of these reserves that started in early 2011, and then went vertical since late 2012.”
While Japan’s economic troubles remain, is it fair to assume that the BOJ’s attempts at stimulus were an abysmal failure? Let’s examine the evidence.
Following is a long-term graph of Japan’s Nikkei stock index. Japan’s attempts at QE started in late 2001 and ended in 2006. Given the downside momentum that had been established in the Nikkei heading into 2001 – 11 years worth to be exact – it took some time before the first effects of the stimulus registered in the stock market. By 2003, however, the Nikkei was on the up-and-up. Japan’s central bank let their foot off the QE accelerator between 2006 and 2001, though, and this explains why the rally didn’t continue further. The 2008 credit crisis only added to the Nikkei’s woes.

Then starting in 2011, the BOJ once again commenced QE at an even more furious pace than before. This led to a much quicker improvement in the Nikkei, which zoomed to its highest level in over a decade. Undoubtedly, Japan’s second attempt at QE would have been far more successful had not the government implemented an ill-advised tax increase. This foolish measure heavily undermined the positive impact of QE and put the brakes on the Nikkei rally. It also put Japan’s economy back into recession for a time.
A lingering problem for the European Union countries since 2008 has been the negative impact of years of misguided austerity policies. European Central Bank (ECB) President Mario Draghi famously pledged years ago the ECB would do “whatever it takes” to reverse the deflationary undercurrents plaguing the euro zone. But until this year the ECB failed to live up to that promise. Late last year Europe’s central bank finally got serious and lowered deposit rates while extending its 80-billion-euro monthly asset purchase program.
Positive results of the bank’s efforts to date haven’t yet been seen, though there are preliminary indications that many European bourses are establishing intermediate-term bottoms. Much depends on the ECB’s commitment to QE in the year ahead. By keeping the proverbial pedal to the floor for an extended length of time, the ECB may yet succeed in reversing the continent’s financial malaise. However, if the bank makes the mistake Japan made by easing up on QE prematurely, the euro zone can expect to see a resumption of the economic malaise.
By far the biggest success story of QE has been the U.S. The Fed’s unprecedented stimulus measures in the wake of the 2008 credit crash galvanized an historic rally in the stock market which brought recovery to the major indices in record time. Since the U.S. essentially has a financial economy, any sustained recovery in financial asset prices must of necessity lift the economy sooner or later. Thus the improvement in many sectors of the economy since 2009 can be attributed, at least in part, to QE.
The evidence to date strongly suggests that stimulus played an integral role in fueling the mighty asset price recovery that began over seven years ago. The Federal Reserve’s interventionary QE program was successful beyond anyone’s wildest guess when measured by the result of the equity and real estate markets. And while many are quick to condemn QE as having been a failure at resuscitating the economy, the data would argue otherwise.
But after about six years of easy money, the Fed brought its QE program to a close in late 2014. After that the stock market as measured by the NYSE Composite Index (NYA), the broadest measure of U.S. equities, entered a prolonged sideways trend, which can largely be attributed to the loss of QE. The loss of billions of dollars per month of liquidity for stocks was gone and with it the sustained forward momentum that fueled the market’s surge from 2009 to 2014.
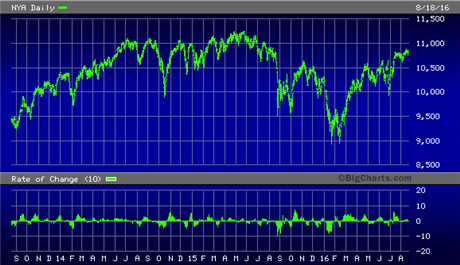
Keeping the U.S. market buoyant since then has been a combination of factors. Continued low interest rates coupled with huge inflows of cash from foreigners seeking a safe haven from the global crisis have been a huge benefit for equities. The lack of competition from commodities and other assets has also helped. This influx of foreign “hot” money has amounted to a de facto stimulus for stocks, so in essence the market is still receiving stimulus from afar.
Stocks need stimulus in order to advance in the absence of a strong economy. When the economy is strong investors need no prodding to put their excess earnings into equities with hopes of greater profits. A strong economy also breeds confidence in the present and optimism about the future; it serves as a kind of natural stimulus for the stock market.
Ironically, central bank stimulus can also serve as a deterrent for small investors since they interpret the need for stimulus as confirmation that the economy is weak and needs assistance. Thus the public sometimes lack the incentive to take risks when QE is in full swing. It’s the professional investor who is sophisticated enough to read between the lines and buy stocks in a weak economy, provided there is stimulus. This is the great paradox of a stimulus-driven bull market: only the few participate, yet it eventually benefits the many as the wealth generated from higher stock prices permeates the broad economy.
The great unknown factor concerning QE is the outer limit of its success. Just how successful can QE be in stimulating the economy? A satisfactory answer to this question hasn’t yet been supplied. Just when it looked like the financial market rebound from the 2009 low was ready to explode into a full-fledged runaway bull, the Fed took its foot off the accelerator. Eventually the generous liquidity the Fed was supplying ground to a halt and the stock market responded accordingly as its forward momentum slowed exceedingly.
Central bankers, it seems, have an inveterate fear of inflation. Most of today’s voting Fed members came of age during the runaway inflation of the 1970s. The memories of that harrowing experience continue to haunt them, and its influence is reflected in their policies. The prevailing belief is that too much QE equates to too much inflation. This is a fallacy. The U.S. and global economies have been so significantly altered by demographic, social and political shifts in the last two decades that inflation won’t be a major concern for many years to come.
The Fed could have doubled its asset purchases between 2009 and 2014 without creating any appreciable increase in inflation. Instead it decided to stop QE before inflation even registered, which was tantamount to pushing a stalled vehicle up a hill only to stop pushing before the summit is reached. It would have been exciting to see just how successful QE could have been had the Fed decided to gun for prosperity. Instead, the Fed chickened out and ruined its best chance at delineating once and for all the outer limits of central bank stimulus.
The other objection to a full-throttle QE initiative is the widespread fear of creating another asset bubble similar to the real estate bubble that popped in 2006 and led to the credit crisis. History and human nature testify that a catastrophic crash of the magnitude of the ’08 credit storm takes at least one entire generation (i.e. circa 20 years) to dissipate. In other words, it takes the advent of an entirely new generation who didn’t experience the crisis to repeat its mistakes. At present there is a complete absence of risk-taking behavior among the generation that experienced 2008. That deep-seated fear of risk won’t disappear anytime soon. Thus the “bubble that broke the world” isn’t going to happen again for a long, long time.
The simple answer to the question, “Can stocks survive without stimulus?” is an emphatic “No!” Stocks always need fresh injections of liquidity to gain ground and surge ahead. Whether the stimulus takes the form of QE, fiscal policy or surplus savings is a moot point. But stimulus in all its many forms must be present to propel equity prices ever higher. And rising stock prices in a financial economy like the U.S. always creates a wealth effect. Thus in the final analysis, stimulus is to everyone’s benefit.
The Stock Market Cycles
For the summer months only, the book “The Stock Market Cycles” is available at a special discount to readers of this commentary. The book reveals the key to interpreting long-term stock price movement and economic performance, namely the famous Kress series of yearly cycles. This work was undertaken based on popular demand and was written in a style that casual readers and experts alike can enjoy and understand. The book covers each one of the yearly cycles in the Kress Cycle series, starting with the 2-year cycle and ending with the 120-year Grand Super Cycle.
The book also covers the K Wave and the effects of long-term inflation/deflation that these cycles exert over stock prices and the economy. Each chapter contains illustrations that show exactly how the yearly cycles influenced stock market performance and explains where the peaks and troughs of each cycle are located and how the cycles can predict future market and economic performance. Order your autographed copy today:
https://www.clifdroke.com/books/Stock_Market.html
Clif Droke is a recognized authority on moving averages and internal momentum. He is the editor of the
Momentum Strategies Report newsletter, published since 1997. He has also authored numerous books covering the fields of economics and financial market analysis. His latest book is
Mastering Moving Averages. For more information visit
www.clifdroke.com